Blockchain technology is arguably the most revolutionary of the many revolutionary ideas that have emerged from the rapid expansion of digital technologies. Although blockchain is frequently linked to cryptocurrencies like Ethereum and Bitcoin, it is much more than just a platform for virtual money. It is a paradigm shift that might completely reinterpret what it means to be transparent, secure, and trustworthy in the digital sphere.
In its most basic form, chain is a distributed, decentralized ledger that keeps track of transactions across numerous computers in a way that makes it impossible to change the recorded transactions later. Because of its decentralization and intrinsic immutability, trust is no longer exclusively dependent on centralized organizations like governments, banks, or businesses. Rather, transparency features, consensus processes, and cryptographic principles all work together to build trust into the system.
This paper investigates how block chain technology is changing trust and transparency in a number of industries, such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, governance, and more. It also looks at the future course of this game-changing technology as well as the difficulties and possible hazards of adopting block chain.
Also Read:https://babni.online/life-insurance/

Understanding Blockchain Technology
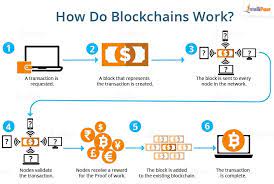
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers, known as nodes. Each “block” in the chain contains a list of transactions that are cryptographically secured and linked to the previous block, forming an immutable chain. This distributed nature means that there is no central authority that controls the network, making it resistant to censorship and tampering.
Among the essential elements of technology are: . Decentralization: Blockchain is based on a dispersed network of computers, as opposed to conventional systems where data is kept in centralized databases under the control of a single organization. This makes transactions quicker, less expensive, and more secure by doing away with the need for reliable middlemen like banks or other third-party organizations.
. Immutability: Without the network’s consent, data cannot be removed or changed once it has been added to the block chain. This guarantees the integrity of the data by producing a clear and long-lasting record of every transaction.
. Cryptography: To protect transactions and guarantee data privacy, blockchain employs sophisticated cryptographic techniques like hashing and public-key encryption. This renders blockchain extremely secure and impervious to tampering.
. Consensus Mechanisms: The network’s participants must agree in order to add new blocks to the blockchain. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Proof of Work (PoW), and Proof of Stake (PoS) are popular consensus techniques that support the blockchain’s security and integrity.
Together, these characteristics form a potent system that guarantees the security and correctness of transactions while also facilitating the development of trustless settings in which users are not dependent on middlemen to confirm or validate their exchanges.
Redefining Trust in a Decentralized World
Human relationship, particularly in the digital age, is based on trust. Trust has always been built through middlemen like governments, banks, and other outside organizations. By serving as reliable arbitrators, these centralized organizations make sure that deals are legal and that parties are operating honestly.
However, there are a number of disadvantages to depending on these middlemen. Systems that are centralized are susceptible to manipulation, fraud, and single points of failure. They can also be expensive, slow, and error-prone. By eliminating the need for middlemen and depending on the network itself to validate transactions, block chain technology addresses a number of these problems.
Block chain’s decentralization enables consumers to have faith in the technology instead of an outside authority. As a result, the system becomes more transparent and inclusive, giving users greater control over their personal information and resources. Blockchain trust is based on consensual processes and cryptographic security, not on the standing of centralized organizations.
Wide-ranging effects result from this move away from centralized trust models and toward decentralized trust. It can decrease the cost and complexity of transactions, empower people, and lessen the influence of strong middlemen. Block chain can speed up and lower the cost of transactions in a variety of sectors, including supply chain management and banking, by doing away with the need for reliable middlemen.
Also Read:https://babni.online/life-insurance/
Blockchain and Transparency
The capacity of blockchain technology to offer transparency is among its most important benefits. Traditional systems frequently lack transparency, requiring consumers to have faith in the sincerity of centralized institutions. On the other side, blockchain provides an open and transparent system in which every transaction is visible to all network users.
All transactions on the block chain are immutable, which means that once they are added, they cannot be removed or changed. Because the block chain permanently stores the history of every transaction, this offers an unprecedented amount of transparency. By enabling users to track the origin of any transaction and confirm its legitimacy, fraud risk is decreased and accountability is guaranteed.
Moreover, block chain’s transparency is not limited to financial transactions. In supply chains, for example, blockchain can track the journey of goods from production to delivery, providing real-time visibility into every step of the process. This can help companies ensure that products are sourced ethically, reduce fraud, and improve efficiency.
1. Blockchain in Financial Transparency
Lack of transparency has always been a problem in the financial industry. Conventional financial systems are frequently opaque, with organizations and people concealed behind intricate procedures and frameworks. However, by enabling transactions to be documented in an unchangeable ledger that is publicly verifiable, block chain provides a more transparent approach.
Transactions between parties are typically concealed behind layers of intermediaries in traditional banking, for instance. By enabling real-time viewing of the same transaction history by all participants, blockchain eliminates this opacity. This can significantly lower the likelihood of money laundering, financial fraud, and other illegal activity. Block chain can aid in restoring the financial system’s credibility by establishing a transparent system, which has been damaged by previous financial crises.
2. Blockchain in Supply Chain Transparency
Block chain has the potential to revolutionize supply chain transparency. Businesses frequently find it difficult to trace the provenance and legitimacy of goods in sectors including manufacturing, food production, and pharmaceuticals. Blockchain makes it possible to track and document each stage of the supply chain, guaranteeing that goods are authentic and obtained ethically.
In the food business, where people are growing more concerned about the safety and quality of the items they eat, this degree of transparency is especially crucial. Businesses may boost customer trust and brand loyalty by utilizing block chain technology to track product journeys and validate ingredient origins.
Also Read:https://babni.online/life-insurance/
Blockchain in Various Sectors
1 Blockchain in Finance: Beyond Cryptocurrency
Although blockchain is most famous for enabling cryptocurrencies like Ethereum and Bitcoin, its uses in finance go much beyond virtual money. For instance, Decentralized Finance (DeFi) uses blockchain technology to offer financial services including trading, lending, and borrowing without relying on conventional financial institutions.
Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement explicitly put into code, are used by DeFi systems to make transactions easier. Usually constructed on blockchain networks such as Ethereum, these platforms enable the development of decentralized financial services that are available to anybody with an internet connection.
DeFi provides reduced fees, quicker transactions, and greater financial inclusion by doing away with middlemen like banks. DeFi provides a means of participating in the global economy without depending on centralized institutions for those in underdeveloped nations who might not have access to regular financial services.
2. Blockchain in Healthcare: Securing Patient Data
Blockchain is a prime candidate to revolutionize healthcare because of its capacity to guarantee data security and integrity. It can be challenging to safely access and share patient data since it is frequently dispersed among several systems and providers. Blockchain can provide privacy and transparency by generating a single, unchangeable record of patient data that is available to authorized parties.
Healthcare practitioners may safely and instantly communicate test results, prescriptions, and medical information by utilizing blockchain technology. This can expedite administrative procedures, lower errors, and enhance patient results. Furthermore, patients can exercise greater control over their personal data by choosing who can access and utilize their medical records.
3 Blockchain in Governance: Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
Blockchain has enormous potential to improve governance’s accountability and openness. A blockchain platform, for instance, may be used to conduct elections, guaranteeing that votes are securely and irrevocably recorded and lowering the possibility of fraud and manipulation.
Blockchain technology might also be used by governments to provide people more insight into public spending. Governments may make sure that public funds are being used effectively and openly by keeping track of every transaction on the blockchain. This might lessen corruption and boost confidence in public institutions.
Also Read:https://babni.online/life-insurance/

Challenges and Pitfalls of Blockchain Adoption
Blockchain technology has drawbacks in spite of its many benefits. Scalability, regulatory unpredictability, and environmental concerns rank highest among these difficulties.
1. Scalability
Only a certain amount of transactions can be processed by blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum per second, which can cause congestion and expensive transaction fees when demand is strong. Although scalability problems are being addressed with solutions like Proof of Stake, layer-2 protocols, and sharding, it is still a major obstacle to broad adoption.
2 Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments and authorities are finding it difficult to keep up with the rapid growth and disruption of blockchain technology across a number of industries. Businesses find it challenging to fully use blockchain and cryptocurrencies due to the uncertainty produced by unclear legislation. Frameworks that strike a balance between innovation and consumer security and protection must be created by governments.
3 Environmental Concerns
Many blockchain networks use a lot of energy since they need a lot of processing power to validate transactions, especially those that use Proof of Work. This has sparked worries about blockchain’s potential effects on the environment, especially in light of climate change. To cut down on energy use and lessen environmental damage, new consensus techniques like Proof of Stake and Proof of Authority are being developed.
The Future of Blockchain
Although blockchain technology is still in its infancy, its potential is obvious. As the technology advances, we anticipate seeing even more creative uses in a variety of sectors, including as smart cities and asset tokenization. The rate at which blockchain technology is adopted will depend on how quickly solutions that address issues of scalability, energy efficiency, and regulations are developed.
In the end, blockchain could revolutionize security, transparency, and trust in the digital era. Blockchain has the potential to establish a more egalitarian and inclusive global economy by removing middlemen, improving data integrity, and offering real-time transaction visibility.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology represents a paradigm shift in how we approach trust, transparency, and security in the digital age. Its decentralized nature, combined with cryptographic security and consensus mechanisms, allows for the creation of systems that operate without the need for intermediaries. This has profound implications for industries ranging from finance to healthcare to governance, enabling greater efficiency, security, and transparency.
Despite the challenges, blockchain has the potential to transform industries, reduce fraud, increase accountability, and empower individuals. As the technology continues to evolve, we are only beginning to see the true scope of its potential. The blockchain revolution is well underway, and it promises to reshape the digital landscape for years to come.